Chronic kidney disease (CKD) causes long-term kidney damage.
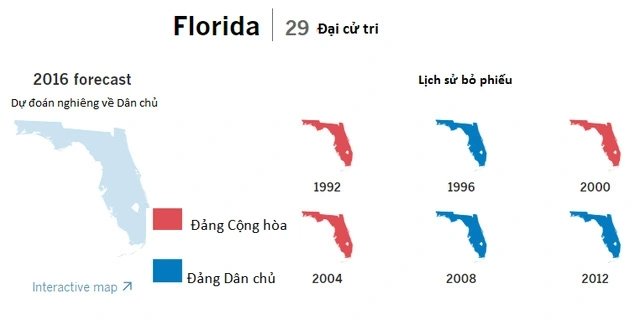
State 1
At this stage, the kidneys are very slightly damaged.
Some lifestyle adjustments can slow the progression of the disease such as: good control of blood sugar and blood pressure (if you have diabetes or high blood pressure), maintaining a healthy, balanced diet.
Phase 2
In stage 2, the kidneys only function from 60 – 89% of normal capacity.
Stage 3
The kidneys will function at 45 – 59% in stage 3A and 30 – 44% in stage 3B.
Chronic kidney disease in stage 3 causes the kidneys to function poorly and begin to accumulate harmful waste and toxins.
At this stage, the patient may experience mild complications such as anemia, bone and joint disease, high blood pressure… Some medications such as high blood pressure drugs and diuretics help reduce symptoms;
Stage 4
Stage 4 also means that the kidneys have suffered moderate to severe damage.
In addition to the same treatment as the previous stages, discuss dialysis and kidney transplant with your doctor if there is a risk of kidney failure.
Stage 5
The kidneys only work below 15% capacity or have kidney failure.
Dialysis is not a treatment for kidney disease but is a process that helps remove waste and fluid from the blood.